Does Price Floor Affect Equilibrium

A price floor or minimum price is a lower limit placed by a government or regulatory authority on the price per unit of a commodity.
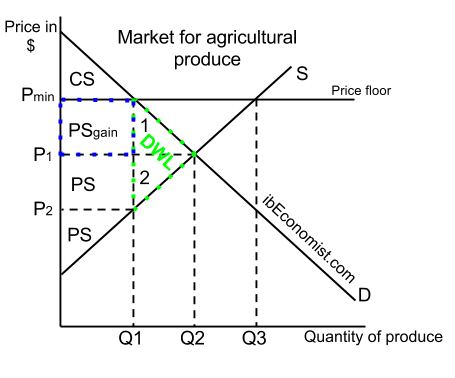
Does price floor affect equilibrium. Governments usually set up a price floor in order to ensure that the market price of a commodity does not fall below a level that would threaten the financial existence of producers of the commodity. A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective. A price ceiling is a legal maximum price but a price floor is a legal minimum price and consequently it would leave room for the price to rise to its equilibrium level. A price floor is a form of price control another form of price control is a price ceiling.
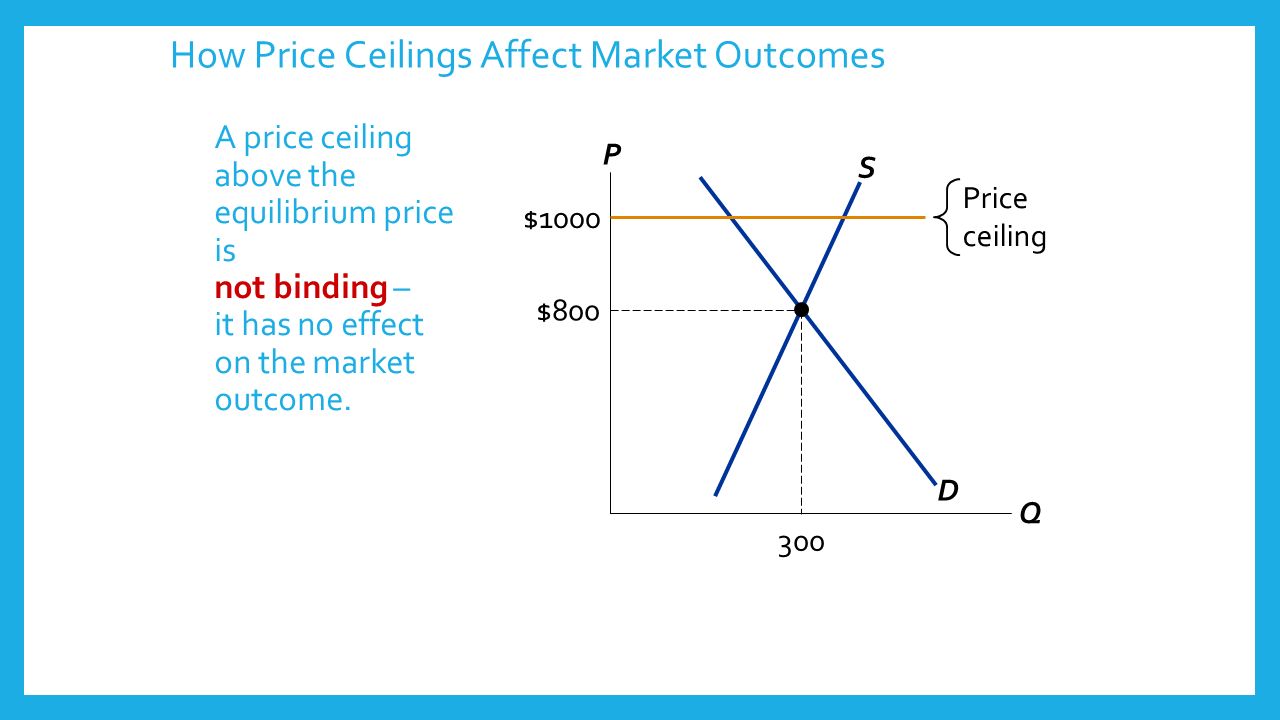
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service. But the price floor p f blocks that communication between suppliers and consumers preventing them from responding to the surplus in a mutually appropriate way. In other words a price floor below equilibrium will not be binding and will have no effect. Minimum wage and price floors.
Government set price floor when it believes that the producers are receiving unfair amount. However price floor has some adverse effects on the market. They are forced to pay higher prices and consume smaller quantities than they would with free market. Price floor is enforced with an only intention of assisting producers.
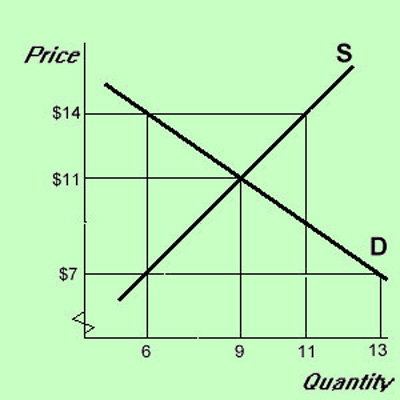
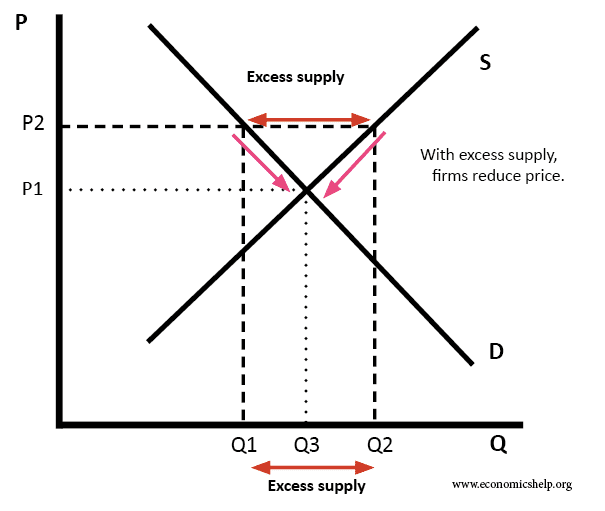
This is a price floor that is less than the current market price. There are two types of price floors. A binding price floor is one that is greater than the equilibrium market price. Taxation and dead weight loss.
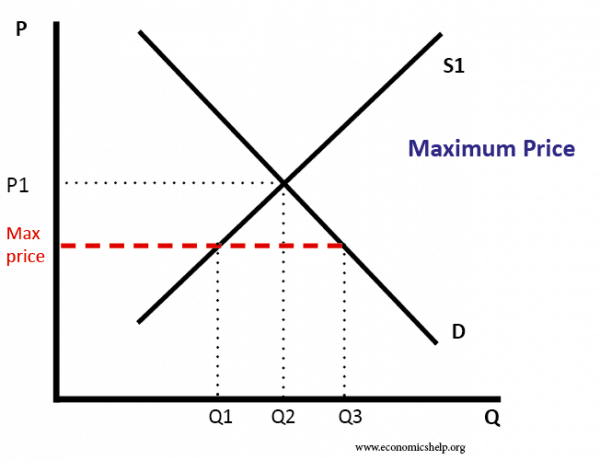
For a price floor to be effective the minimum price has to be higher than the equilibrium price. Price floors are only an issue when they are set above the equilibrium price since they have no effect if they are set below market clearing price. This is the currently selected item. Suppliers can be worse off.
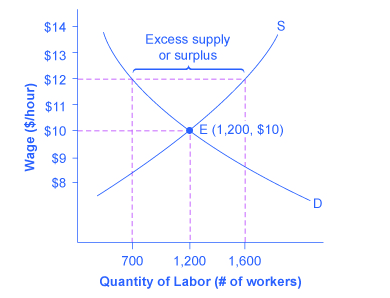
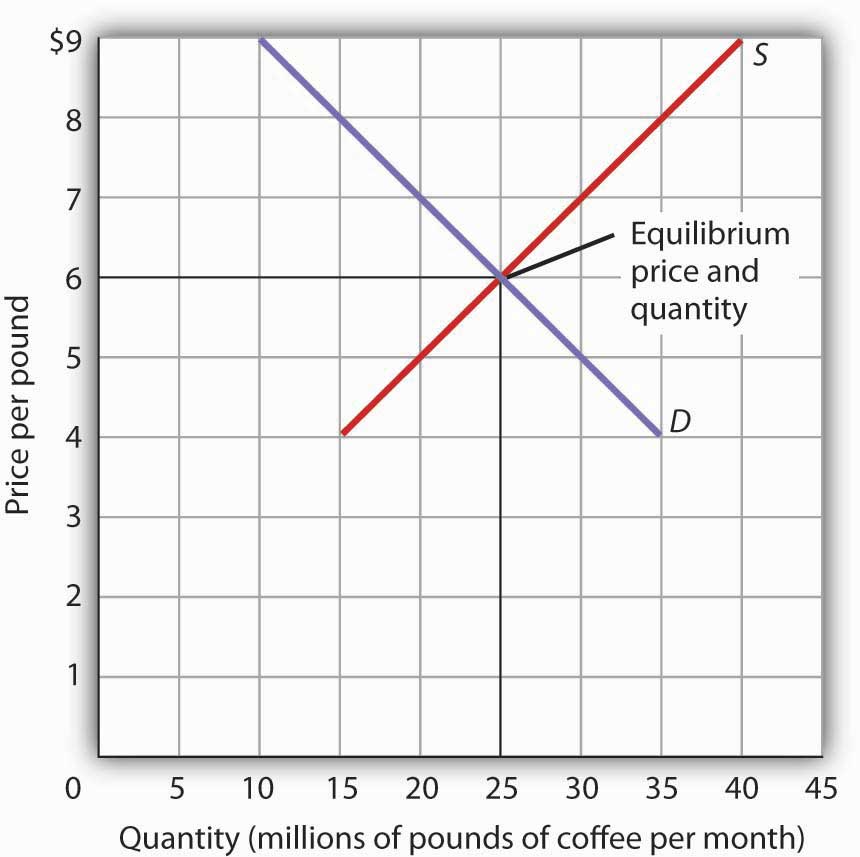
Types of price floors. For example many governments intervene by establishing price floors to ensure that farmers make enough money by guaranteeing a minimum price that their goods can be sold for. The most common example of a price floor is the minimum wage. The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.
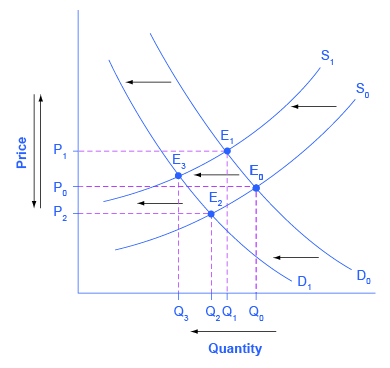
That will create a surplus. Consumers are clearly made worse off by price floors. When they are set above the market price then there is a possibility that there will be an excess supply or a surplus. The effect of government interventions on surplus.
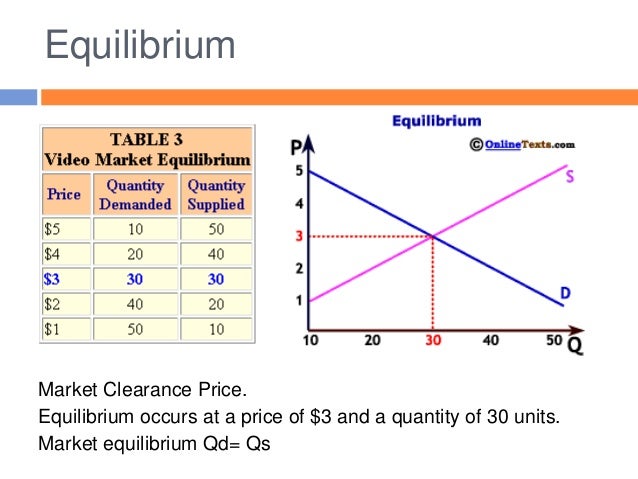
Example breaking down tax incidence. How does a price floor set above the equilibrium level affect quantity demanded and quantity supplied. Price and quantity controls. If price floor is less than market equilibrium price then it has no impact on the economy.
Price ceilings and price floors.



























:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/WhyYouCantInfluenceGasPrices3-257334e47bc54cd7a449da9df90814af.png)




/disequilibrium-498e9ba4154c4a7c8739b3443da14b17.png)